Usually. Experienced observers can almost always identify these species correctly based on careful judgment of head shape and bill size, but these are subtle and subjective impressions, and require a foundation of experience and/or direct comparisons with Sooty. Other features can offer supportive clues or draw attention to a potential Short-tailed, but are not very reliable on their own.
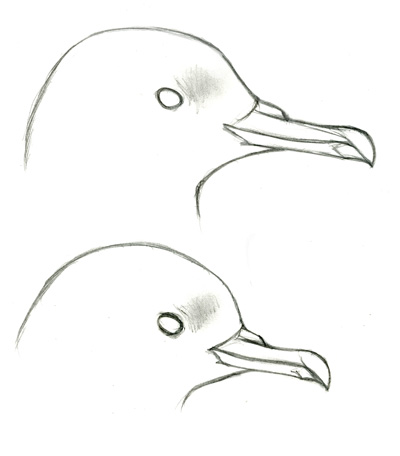
Short-tailed vs Sooty Shearwater
These two species are clearly among the most difficult species-pairs to identify. Differences are small and subjective, and the birds are usually seen in flight and at a distance, often from an unstable boat deck. Their overall similarity is shown by the fact that only a few field marks have ever been proposed.
- rounder head and shorter bill – Short-tailed usually appears “cuter”, with a slightly steeper forehead, more rounded crown, and smaller bill, best appreciated on a swimming bird at close range
- darker underwing coverts – fairly reliable, slightly darker and more uniform on Short-tailed, but the color in both species is variable, with a silvery sheen, and is profoundly influenced by lighting. Furthermore it can be extremely difficult to see clearly, with wings often flickering in and out of shadow.
- narrower wing shape – slightly narrower wings (and quicker wingbeats) on Short-tailed, but this is extremely subtle and subjective, and dependent on weather conditions and flight style
- smaller overall size – slightly smaller overall, but with all the usual cautions about the difficulty of judging size
- darker head and paler chin – Short-tailed sometimes looks obviously dark-hooded with pale chin, unlike the more uniform color of Sooty, but not always, and this impression varies depending on lighting
- shorter tail (?) – feet often project beyond tail tip in flight, which is seen less often on Sooty Shearwater. Both species often tuck their legs into the flank feathers when flying, so a lack of toes beyond the tail means nothing. (Note that measurements do not really support the “shorter tail” hypothesis, the toe projection may be the result of slightly longer legs, or it may have another explanation)
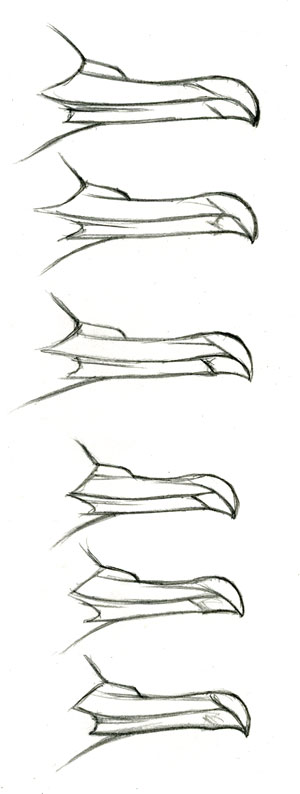
Of these six features, only head and bill shape offer the promise of a consistent and reliable field mark that might convince a records committee of the identity of a Short-tailed Shearwater outside its normal range. This requires high-quality views from close range, preferably of a bird swimming on the water (not flying).
Bill shape and size
My study of specimens at MCZ ((Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University)) shows that there is actually no appreciable difference in bill shape. Proportions of nostril tubes, shape of feathering at bill base, size of the nail, etc. is all identical. The only difference is in bill length (and a very subtle difference in relative thickness, see below). The drawings at right show three bills of each species, traced from specimens and adjusted to the mean length of that species. Subtle differences in individuals make each bill look a little different, but if we ignore overall size it is impossible to distinguish Sooty from Short-tailed.
Measurements (from Pyle 2008) show that Short-tailed averages about 24% shorter-billed than Sooty with no overlap in measurements: Short-tailed 29-35 mm, Sooty 38-46 mm. In practice, however, the difference is less obvious because Short-tailed is a smaller bird overall.
| Short-tailed Shearwater measurements expressed as a percentage of Sooty Shearwater measurements: | |
|---|---|
| wing | 91% |
| tail | 89% |
| tarsus | 93% |
| bill length | 76% |
| bill depth | 82% |
If we could enlarge the body of Short-tailed Shearwater to match Sooty in wing, tail, and tarsus measurements, the bill would still be shorter – about 84% as long as Sooty. This is a significant difference and should be apparent under good views in the field, but not as much as the 76% value the absolute bill measurements would suggest. Furthermore, when this correction for body proportions is applied, there is overlap in the apparent bill length relative to body size.
Bill depth is about 20% smaller in Short-tailed than Sooty, while bill length is 24% smaller, so the bill of Short-tailed is proportionally thicker. In other words, if we enlarged the bill of a Short-tailed to be the same length as a Sooty’s, it’s bill depth would average about 8% thicker than Sooty. ((Obviously the former common name of Slender-billed Shearwater was incorrect. The new name – Short-tailed – is not much better, since the tail is no shorter than Sooty’s relative to the rest of the body.)) While a difference of this magnitude is often visible in the field, a relative difference like this requires a careful assessment of bill proportions, making mental adjustments for overall size, and in actual field conditions this relative difference is probably of little value.
Interestingly, while looking at specimens I was fairly certain that the difference in bill length was due to a reduction of the length of the mid-section of the bill of Short-tailed – that the nasal tubes and nail were similar on the two species, but Sooty had an elongated middle section. Tracing bill shapes and overlaying them showed conclusively that this was not true, and that the proportional lengths of bill parts of both species were the same. But my impression of a shorter mid-section persists even in the drawings shown here. I think the explanation is that this is due to the relatively thicker bill of Short-tailed, and what I interpreted as a shorter mid-section relative to the tubes and nail is actually a shorter mid-section relative to the bill depth.
Head shape
It has often been noted that Short-tailed has a steeper forehead and more rounded head than Sooty, and this is certainly a very consistent impression in the field. The skulls of the two species do not show a difference in forehead angle, but Sooty does show a slightly longer forehead to match the longer bill (photos of Short-tailed skull here and photos of Sooty here). In practice this difference in head shape can be striking, but variation in the attitude of the individual bird, different angles of view, etc mean that it is common to find a Sooty that appears momentarily very round-headed and small-billed.
The differences in head shape are subtle and subjective. There is no quantifiable, objective difference in head shape that can be used to distinguish the two species. A significant effect of the steep forehead is to enhance the small-billed appearance of Short-tailed. The interaction of head shape and apparent bill size cannot be overemphasized, and the two things must be considered together. A bird with a small bill will appear round-headed, and vice versa. A Sooty with its forehead feathers fluffed, or seen from an angle that makes the forehead appear steep, will look shorter-billed than one with the forehead sloped. So, while measurements suggest that Short-tailed and Sooty Shearwater can be very similar in bill length, the slightly shorter bill, in concert with the slightly steeper forehead, creates a distinctly different impression.
Conclusions
Experienced observers within the normal range of Short-tailed Shearwater can identify the species with reasonable confidence, even at a distance, by subtle clues of shape, size, color, and season, but such identifications will never reach the highest level of confidence. These are educated guesses and are easily influenced by all of the pitfalls of expectations and confirmation bias.
Identifying the species with a higher level of confidence requires close and prolonged views, and should focus on bill proportions. Judging this will require previous experience with Sooty and/or Short-tailed Shearwater, and ideally should be based on direct comparisons between the bird in question and Sooty Shearwater.
In the end the most reliable difference seems to be the gestalt impression of the overall head and bill proportions – an inherently unreliable feature, but one that experienced birders will be comfortable using.
References
Gillson, G. 2001. Separation of Sooty and Short-tailed Shearwaters. http://thebirdguide.com/pelagics/book/id_sosh_stsh.htm
Gillson, G. 2008. Field separation of Sooty and Short-tailed Shearwaters off the west coast of North America. Birding 40:34-40. http://www.aba.org/birding/v40n2p34.pdf
Pyle, P. 2008. Identification Guide to North American Birds. Part II. Slate Creek Press.


Hi David
a fantastic work as fantastic is all your work and webpage…
many compliments from Sicily !!
THANKS
Andrea
Anyone fancy a go at identifying this bird photographed from a beach in Guangdong Province in Southern China in May (where Swinhoe’s Plovers breed incidentally), where we can be pretty certain its not a Balearic!
There is more info on the the status of various species in S China and the circumstances of the record on that page
http://www.birdforum.net/showthread.php?t=203796
Any views most welcome.
Cheers
Mike Kilburn
(Hong Kong)
Excellent treatment, David. I would suggest more emphasis a behavioral clue—the difference is flight pattern. This was first pointed out to me by Steve Howell on a Cordell Bank trip in October and I found it very helpful. The Short-tailed flight is “snappier” (Steve’s term), with a more abrupt series of downstrokes interspersed with the gliding on fixed wings characteristic of both species. In California, at least, both species occur together in late fall offering nice opportunities for comparison.